Differenze tra le versioni di "Gruppo Meteo/HowTo/DebugAVR"
| (17 versioni intermedie di 2 utenti non mostrate) | |||
| Riga 1: | Riga 1: | ||
| − | '''Come debuggare con AVR Dragon su arduino | + | '''Come debuggare con AVR Dragon su arduino''' |
WARNING | WARNING | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
It is possible, using the tools discussed here to either ‘brick’ your processor or physically destroy it. This also includes your AVR Dragon. Make sure you double and triple check all connections BEFORE you turn on any power and make sure you disconnect the power BEFORE making any wiring changes. | It is possible, using the tools discussed here to either ‘brick’ your processor or physically destroy it. This also includes your AVR Dragon. Make sure you double and triple check all connections BEFORE you turn on any power and make sure you disconnect the power BEFORE making any wiring changes. | ||
I can not be held responsible for your errors in skills or judgement. | I can not be held responsible for your errors in skills or judgement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Microduino e platformio = | ||
| + | |||
| + | == materiali necessari == | ||
| + | hardware: | ||
| + | * Microduino core/core+ | ||
| + | * AVR Dragon (sostituito da https://www.mouser.it/new/microchip/microchip-atmel-ice-kit/ ?) | ||
| + | * cavi ... | ||
| + | * un pc | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://atmega32-avr.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/AVR_Dragon_Manual_User_Guide.pdf | ||
| + | https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/devicedoc/atmel-42723-avr-dragon_userguide.pdf | ||
| + | |||
| + | software: | ||
| + | * un sistema operativo serio (Linux) | ||
| + | * platformio | ||
| + | * avrdude | ||
| + | * avarice | ||
| + | * gdb | ||
| + | * ddd | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Operazioni sistemistiche preliminari == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Queste operazioni sono necessarie per rendere disponibile AVR Dragon agli utenti abilitati (quelli del gruppo '''dialout'''); altrimenti sarà solo root a poter agire. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Istruzioni valide per Fedora, per altro non so. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Da utente root: | ||
| + | |||
| + | editare il file /etc/udev/rules.d/50-avrdragon.rules e inserire: | ||
| + | |||
| + | SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="03eb", ATTR{idProduct}=="2107", GROUP="dialout", MODE="0660" | ||
| + | |||
| + | oppure utilizzare il default per platformio: | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://docs.platformio.org/en/latest/faq.html#platformio-udev-rules | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | eseguire: | ||
| + | |||
| + | service systemd-udevd restart | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Collegamenti == | ||
| + | '''ISP:''' | ||
| + | In System Programming using SPI is well suited for programming devices soldered onto external target boards. This section explains how to connect the Atmel AVR Dragon to SPI program an external target. The SPI lines are equipped with level converters that automatically will level shift the AVR Dragon signals to the target board voltage. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is recommended that a 6-pin header connector with 2.54mm (100 MIL) spacing is placed on the target board to allow easy access to the SPI programming interface. The following pinout should be used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6pin Header Connector with 2.54mm (100 MIL) spacing | ||
| + | http://www.atmel.no/webdoc/avrdragon/images/ISPHEADER.jpg | ||
| + | |||
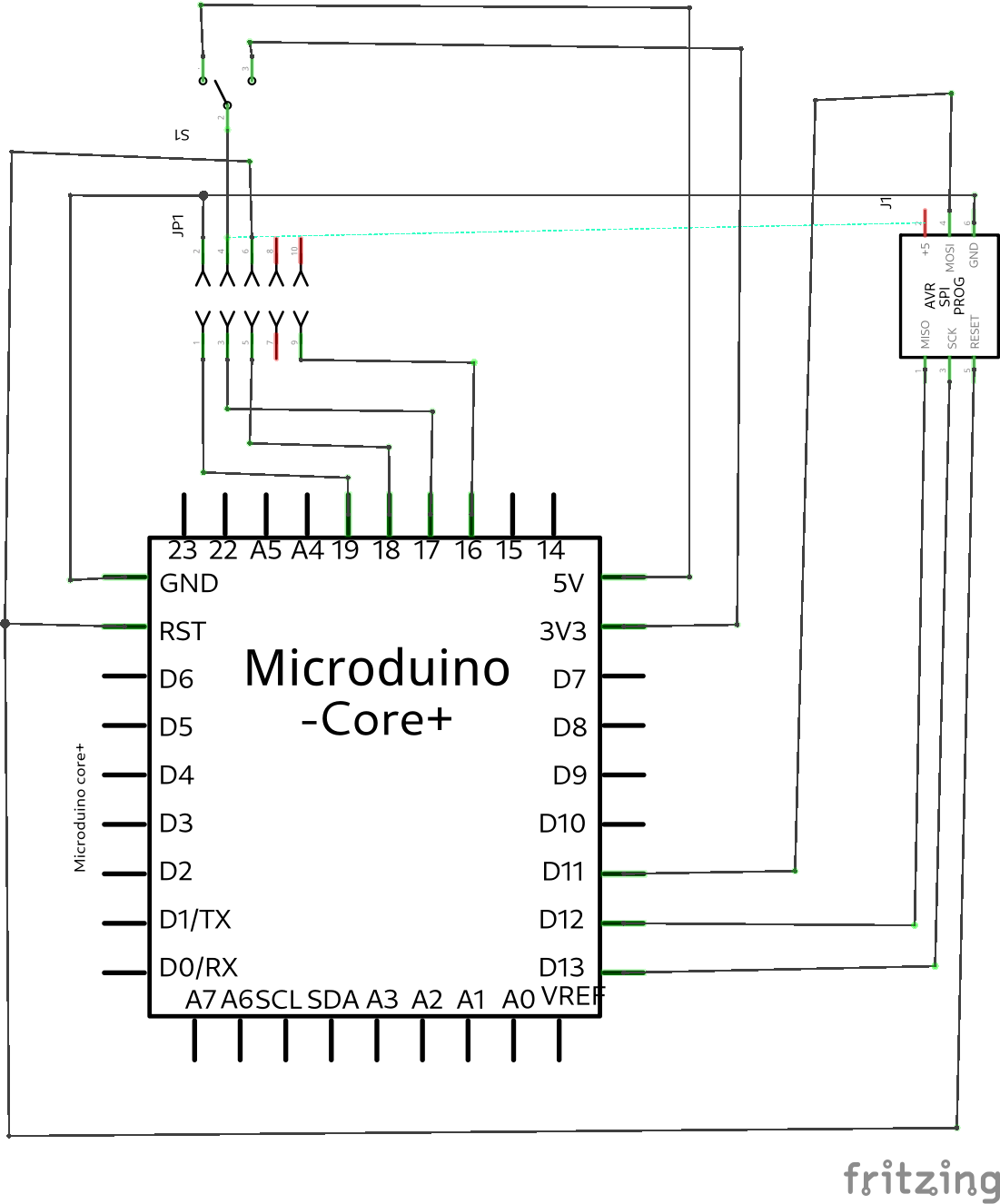
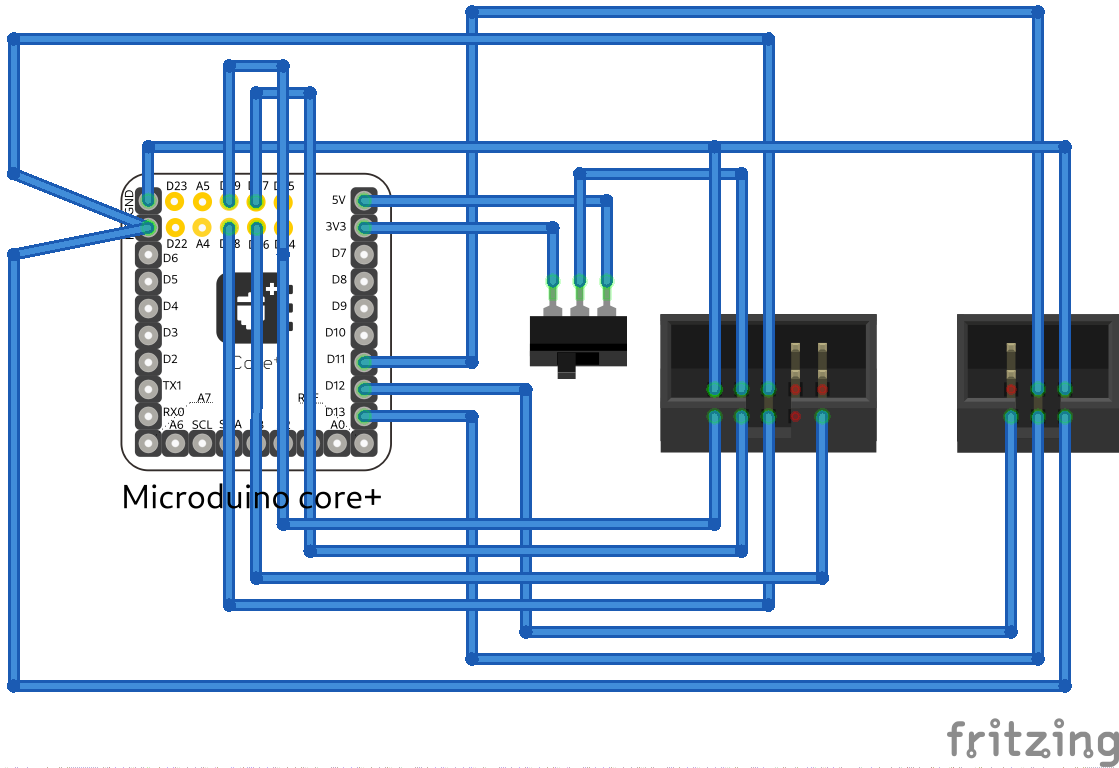
| + | [[File:jtag_isp_schema.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Jtag:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://support.atmel.no/knowledgebase/avrstudiohelp/mergedProjects/AVRDragon/JTAG_schematic_target.JPG | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are only 7 connections needed and these are as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" | ||
| + | |MicroduinoPin | ||
| + | |Signal | ||
| + | |Dragon Jtag | ||
| + | |I/O | ||
| + | |Description | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5v/3.3v | ||
| + | | +5v/+3.3v | ||
| + | |4 | ||
| + | |Output | ||
| + | |5v Supply from Arduino | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND | ||
| + | |GND | ||
| + | |2 or 10 (either will do) | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | |Ground reference | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |D19 (no upin27, in extension for core+) | ||
| + | |TCK | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |Input | ||
| + | |Test Clock, clock signal from AVR Dragon to target JTAG port | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |D18 (no upin27, in extension for core+) | ||
| + | |TMS | ||
| + | |5 | ||
| + | |Input | ||
| + | |Test Mode Select, mode select signal from AVR Dragon to target JTAG port | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |D17 (no upin27, in extension for core+) | ||
| + | |TDO | ||
| + | |3 | ||
| + | |Output | ||
| + | |Test Data Output, data signal from target JTAG port to AVR Dragon | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |D16 (no upin27, in extension for core+) | ||
| + | |TDI | ||
| + | |9 | ||
| + | |Input | ||
| + | |Test Data Input, data signal from AVR Dragon to target JTAG port | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |reset | ||
| + | |RST | ||
| + | |6 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Reset | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: These pin numbers refer to the shield pin numbers of the Microduino core+ and not to the pins on the processor. | ||
| + | Note: Although the +5v are joined, you will still need to provide power to your Mega board by any of the normal methods. The sole purpose of the +5v connection is to correctly configure the level shifters/converts used by the Dragon to process signals between the boards. If you are using a 3.3v Dragon, then it is important that you connect the +5v signal to the +3.3v signal instead. Otherwise there is a pretty good chance you will destroy your Mega in a few seconds. This signal can not power the Mega from the Dragon! | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: Power up your Mega board before the Dragon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: Make sure there are no other connections to pine D16, D17, D18 or D19 on the Microduino, other than those to the Dragon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:jtag_isp.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Fuse Setting == | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://www.codingwithcody.com/2011/04/arduino-default-fuse-settings/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''default Arduino ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Low Fuse 0xFF | ||
| + | * High Fuse 0xDE | ||
| + | * Extended Fuse 0xFD | ||
| + | |||
| + | you need to enable the OCDEN and JTAGEN fuses | ||
| + | |||
| + | Per il calcolo si può utilizzare: | ||
| + | http://www.engbedded.com/fusecalc/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | o anche questo che calcola anche i lock bits: | ||
| + | https://eleccelerator.com/fusecalc/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | da cui si ottiene: | ||
| + | * Low Fuse 0xFF | ||
| + | * High Fuse 0x1E | ||
| + | * Extended Fuse 0xFD | ||
| + | |||
| + | quindi: | ||
| + | |||
| + | avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0x1E:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m | ||
| + | |||
| + | Quando avari finito tutto reimpostare i valori di dafault: | ||
| + | |||
| + | avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0xDE:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m | ||
| + | |||
| + | se invece usi digitecoboot di 4k di dimensione: | ||
| + | |||
| + | avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0x18:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m | ||
| + | |||
| + | Quando avari finito tutto reimpostare i valori di dafault: | ||
| + | |||
| + | avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0xD8:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Sessione di debug == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dopo aver compilato con le opzioni di debug determinati dall'opzione | ||
| + | build_type = debug | ||
| + | |||
| + | in platformio.ini | ||
| + | |||
| + | pio run -t upload | ||
| + | |||
| + | eseguire avarice che rimane in attesa di connessione da parte di gdb: | ||
| + | |||
| + | avarice --dragon --reset-srst :4242 | ||
| + | |||
| + | poi lanciare il debugger: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~/.platformio/packages/toolchain-atmelavr/bin/avr-gdb firmware.elf | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''oppure ddd''' | ||
| + | ddd --debugger ~/.platformio/packages/toolchain-atmelavr/bin/avr-gdb .pio/build/644pa16m/firmware.elf | ||
| + | |||
| + | At the (gdb) prompt, tell GDB to connect to AVaRICE: | ||
| + | |||
| + | (gdb) target remote localhost:4242 | ||
| + | |||
| + | This will stop the program running on the APM and tell you where it stopped: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Remote debugging using localhost:4242 | ||
| + | 0x00002992 in AP_GPS_NMEA::read (this=0x8007aa) | ||
| + | at /Volumes/Data/Users/msmith/work/Mike/ArduPilot/Sketchbook/libraries/AP_GPS/AP_GPS_NMEA.cpp:72 | ||
| + | 72 numc = _port-> | ||
| + | available(); | ||
| + | (gdb) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Use the ‘continue’ command to start the program running again, and hit control-C to stop it once more. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Come far tornare l'arduino come un vero arduino con il suo bootloader == | ||
| + | |||
| + | avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -e -u -U lock:w:0xFF:m -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0xDE:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m | ||
| + | avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -V -U flash:w:optiboot_atmega1280.hex | ||
| + | avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lock:w:0xCF:m | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first command unlocks the bootloader section and sets the fuses. | ||
| + | The second writes the bootloader to the flash memory. | ||
| + | And the third locks the bootloader section again. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Using digitecoboot the commands are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -e -u -U lock:w:0xFF:m -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0xD8:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m | ||
| + | avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -V -U flash:w:optiboot_atmega1280.hex | ||
| + | avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lock:w:0xCF:m | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Arduino mega2560 = | ||
== materiali necessari == | == materiali necessari == | ||
Versione attuale delle 19:50, 14 dic 2021
Come debuggare con AVR Dragon su arduino
WARNING
It is possible, using the tools discussed here to either ‘brick’ your processor or physically destroy it. This also includes your AVR Dragon. Make sure you double and triple check all connections BEFORE you turn on any power and make sure you disconnect the power BEFORE making any wiring changes.
I can not be held responsible for your errors in skills or judgement.
Microduino e platformio
materiali necessari
hardware:
- Microduino core/core+
- AVR Dragon (sostituito da https://www.mouser.it/new/microchip/microchip-atmel-ice-kit/ ?)
- cavi ...
- un pc
https://atmega32-avr.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/AVR_Dragon_Manual_User_Guide.pdf https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/devicedoc/atmel-42723-avr-dragon_userguide.pdf
software:
- un sistema operativo serio (Linux)
- platformio
- avrdude
- avarice
- gdb
- ddd
Operazioni sistemistiche preliminari
Queste operazioni sono necessarie per rendere disponibile AVR Dragon agli utenti abilitati (quelli del gruppo dialout); altrimenti sarà solo root a poter agire.
Istruzioni valide per Fedora, per altro non so.
Da utente root:
editare il file /etc/udev/rules.d/50-avrdragon.rules e inserire:
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="03eb", ATTR{idProduct}=="2107", GROUP="dialout", MODE="0660"
oppure utilizzare il default per platformio:
https://docs.platformio.org/en/latest/faq.html#platformio-udev-rules
eseguire:
service systemd-udevd restart
Collegamenti
ISP: In System Programming using SPI is well suited for programming devices soldered onto external target boards. This section explains how to connect the Atmel AVR Dragon to SPI program an external target. The SPI lines are equipped with level converters that automatically will level shift the AVR Dragon signals to the target board voltage.
It is recommended that a 6-pin header connector with 2.54mm (100 MIL) spacing is placed on the target board to allow easy access to the SPI programming interface. The following pinout should be used.
6pin Header Connector with 2.54mm (100 MIL) spacing http://www.atmel.no/webdoc/avrdragon/images/ISPHEADER.jpg
Jtag:
There are only 7 connections needed and these are as follows:
| MicroduinoPin | Signal | Dragon Jtag | I/O | Description |
| 5v/3.3v | +5v/+3.3v | 4 | Output | 5v Supply from Arduino |
| GND | GND | 2 or 10 (either will do) | - | Ground reference |
| D19 (no upin27, in extension for core+) | TCK | 1 | Input | Test Clock, clock signal from AVR Dragon to target JTAG port |
| D18 (no upin27, in extension for core+) | TMS | 5 | Input | Test Mode Select, mode select signal from AVR Dragon to target JTAG port |
| D17 (no upin27, in extension for core+) | TDO | 3 | Output | Test Data Output, data signal from target JTAG port to AVR Dragon |
| D16 (no upin27, in extension for core+) | TDI | 9 | Input | Test Data Input, data signal from AVR Dragon to target JTAG port |
| reset | RST | 6 | Reset |
Note: These pin numbers refer to the shield pin numbers of the Microduino core+ and not to the pins on the processor. Note: Although the +5v are joined, you will still need to provide power to your Mega board by any of the normal methods. The sole purpose of the +5v connection is to correctly configure the level shifters/converts used by the Dragon to process signals between the boards. If you are using a 3.3v Dragon, then it is important that you connect the +5v signal to the +3.3v signal instead. Otherwise there is a pretty good chance you will destroy your Mega in a few seconds. This signal can not power the Mega from the Dragon!
Note: Power up your Mega board before the Dragon.
Note: Make sure there are no other connections to pine D16, D17, D18 or D19 on the Microduino, other than those to the Dragon.
Fuse Setting
http://www.codingwithcody.com/2011/04/arduino-default-fuse-settings/
default Arduino
- Low Fuse 0xFF
- High Fuse 0xDE
- Extended Fuse 0xFD
you need to enable the OCDEN and JTAGEN fuses
Per il calcolo si può utilizzare: http://www.engbedded.com/fusecalc/
o anche questo che calcola anche i lock bits: https://eleccelerator.com/fusecalc/
da cui si ottiene:
- Low Fuse 0xFF
- High Fuse 0x1E
- Extended Fuse 0xFD
quindi:
avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0x1E:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m
Quando avari finito tutto reimpostare i valori di dafault:
avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0xDE:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m
se invece usi digitecoboot di 4k di dimensione:
avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0x18:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m
Quando avari finito tutto reimpostare i valori di dafault:
avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0xD8:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m
Sessione di debug
Dopo aver compilato con le opzioni di debug determinati dall'opzione
build_type = debug
in platformio.ini
pio run -t upload
eseguire avarice che rimane in attesa di connessione da parte di gdb:
avarice --dragon --reset-srst :4242
poi lanciare il debugger:
~/.platformio/packages/toolchain-atmelavr/bin/avr-gdb firmware.elf
oppure ddd
ddd --debugger ~/.platformio/packages/toolchain-atmelavr/bin/avr-gdb .pio/build/644pa16m/firmware.elf
At the (gdb) prompt, tell GDB to connect to AVaRICE:
(gdb) target remote localhost:4242
This will stop the program running on the APM and tell you where it stopped:
Remote debugging using localhost:4242 0x00002992 in AP_GPS_NMEA::read (this=0x8007aa) at /Volumes/Data/Users/msmith/work/Mike/ArduPilot/Sketchbook/libraries/AP_GPS/AP_GPS_NMEA.cpp:72 72 numc = _port-> available(); (gdb)
Use the ‘continue’ command to start the program running again, and hit control-C to stop it once more.
Come far tornare l'arduino come un vero arduino con il suo bootloader
avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -e -u -U lock:w:0xFF:m -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0xDE:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -V -U flash:w:optiboot_atmega1280.hex avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lock:w:0xCF:m
The first command unlocks the bootloader section and sets the fuses. The second writes the bootloader to the flash memory. And the third locks the bootloader section again.
Using digitecoboot the commands are:
avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -e -u -U lock:w:0xFF:m -U lfuse:w:0xFF:m -U hfuse:w:0xD8:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -V -U flash:w:optiboot_atmega1280.hex avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p m1284p -U lock:w:0xCF:m
Arduino mega2560
materiali necessari
hardware:
- arduino mega2560
- AVR Dragon
- cavi ...
- un pc
software:
- un sistema operativo serio (Linux)
- toolchain gcc per avr
- avrdude
- avarice
- gdb
- ddd
Operazioni sistemistiche preliminari
Queste operazioni sono necessarie per rendere disponibile AVR Dragon agli utenti abilitati (quelli del gruppo dialout); altrimenti sarà solo root a poter agire.
Istruzioni valide per Fedora, per altro non so.
Da utente root:
editare il file /etc/udev/rules.d/50-avrdragon.rules e inserire:
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="03eb", ATTR{idProduct}=="2107", GROUP="dialout", MODE="0660"
eseguire:
service systemd-udevd restart
Collegamenti
ISP: In System Programming using SPI is well suited for programming devices soldered onto external target boards. This section explains how to connect the Atmel AVR Dragon to SPI program an external target. The SPI lines are equipped with level converters that automatically will level shift the AVR Dragon signals to the target board voltage.
It is recommended that a 6-pin header connector with 2.54mm (100 MIL) spacing is placed on the target board to allow easy access to the SPI programming interface. The following pinout should be used.
6pin Header Connector with 2.54mm (100 MIL) spacing http://www.atmel.no/webdoc/avrdragon/images/ISPHEADER.jpg
Questo la disposizione dei pin sulla board Arduino http://arduino-info.wikispaces.com/file/view/Mega2560_R3_Label-small-v2%20%282%29.png/471429496/800x526/Mega2560_R3_Label-small-v2%20%282%29.png
il collegamento ISP una volta capito è facile: l'ordine è il medesimo, basta trovare il pin 1 del connettore.
link: http://www.atmel.no/webdoc/avrdragon/avrdragon.isp_description.html http://arduino-info.wikispaces.com/MegaQuickRef
Jtag:
There are only 7 connections needed and these are as follows:
| arduinoPin | Signal | Dragon Jtag | I/O | Description |
| 5v | +5v | 4 | Output | 5v Supply from Arduino |
| GND | GND | 2 or 10 (either will do) | - | Ground reference |
| analog in 4 | TCK | 1 | Input | Test Clock, clock signal from AVR Dragon to target JTAG port |
| analog in 5 | TMS | 5 | Input | Test Mode Select, mode select signal from AVR Dragon to target JTAG port |
| analog in 6 | TDO | 3 | Output | Test Data Output, data signal from target JTAG port to AVR Dragon |
| analog in 7 | TDI | 9 | Input | Test Data Input, data signal from AVR Dragon to target JTAG port |
| reset | RST | 6 | Reset |
Note: These pin numbers refer to the shield pin numbers of the Arduino Mega2560 and not to the pins on the processor. Note: Although the +5v are joined, you will still need to provide power to your Mega board by any of the normal methods. The sole purpose of the +5v connection is to correctly configure the level shifters/converts used by the Dragon to process signals between the boards. If you are using a 3.3v Dragon, then it is important that you connect the +5v signal to the +3.3v signal instead. Otherwise there is a pretty good chance you will destroy your Mega in a few seconds. This signal can not power the Mega from the Dragon!
Note: Power up your Mega board before the Dragon.
Note: Make sure there are no other connections to pine 4, 5, 6 or 7 on the Mega, other than those to the Dragon.
Fuse Setting
http://www.codingwithcody.com/2011/04/arduino-default-fuse-settings/
default Arduino Mega 2560
- Low Fuse 0xFF
- High Fuse 0xD8
- Extended Fuse 0xFD
you need to enable the OCDEN and JTAGEN fuses
Per il calcolo si può utilizzare: http://www.engbedded.com/fusecalc/
da cui si ottiene: -U lfuse:w:0xff:m -U hfuse:w:0x18:m -U efuse:w:0xfd:m
quindi:
avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p atmega2560 -U lfuse:w:0xff:m -U hfuse:w:0x18:m -U efuse:w:0xfd:m
Quando avari finito tutto reimpostare i valori di dafault:
avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p atmega2560 -U lfuse:w:0xff:m -U hfuse:w:0xf8:m -U efuse:w:0xfd:m
Sessione di debug
Dopo aver compilato (io uso ino) con l'opzione -g e preferibilmente con -g2 -O0 caricare il programma usanto l'interfaccia jstag e il Dragon:
avrdude -p atmega2560 -c dragon_isp -P usb -U flash:w:.build/mega2560/firmware.hex:i
eseguire avarice che rimane in attesa di connessione da parte di gdb:
avarice --dragon :4242
poi lanciare il debugger:
avr-gdb .build/mega2560/firmware.elf
attenzione !! ddd non funziona e chissà perchè
ddd --debugger avr-gdb .build/mega2560/firmware.elf
At the (gdb) prompt, tell GDB to connect to AVaRICE:
(gdb) target remote localhost:4242
This will stop the program running on the APM and tell you where it stopped:
Remote debugging using localhost:4242 0x00002992 in AP_GPS_NMEA::read (this=0x8007aa) at /Volumes/Data/Users/msmith/work/Mike/ArduPilot/Sketchbook/libraries/AP_GPS/AP_GPS_NMEA.cpp:72 72 numc = _port-> available(); (gdb)
Use the ‘continue’ command to start the program running again, and hit control-C to stop it once more.
Come far tornare l'arduino come un vero arduino
avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p atmega2560 -e -u -U lock:w:0x3F:m -U efuse:w:0xFD:m -U hfuse:w:0xD8:m -U efuse:w:0xFF:m avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p atmega2560 -V -U flash:w:/usr/share/arduino/hardware/arduino/bootloaders/stk500v2/stk500boot_v2_mega2560.hex avrdude -c dragon_isp -P usb -p atmega2560 -U lock:w:0x0F:m
The first command unlocks the bootloader section and sets the fuses. The second writes the bootloader to the flash memory. And the third locks the bootloader section again.