Differenze tra le versioni di "Raspberry Pi Access Point WEP2"
| Riga 81: | Riga 81: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | Rimane solo un problema sulla risoluzione del nome macchina (hostname) di questo pc, al momento ho risolto sistemando il file "/etc/hosts" in questo modo dove ho modificato la penultima ed aggiunto l'ultima riga (esempio reale preso da [[Centralina livello 1]]): | + | Rimane solo un problema sulla risoluzione del nome macchina (hostname) di questo pc, al momento ho risolto sistemando il file "/etc/hosts" in questo modo, dove ho modificato la penultima ed aggiunto l'ultima riga (esempio reale preso da [[Centralina livello 1]]): |
<pre style="color:green;overflow:auto"> | <pre style="color:green;overflow:auto"> | ||
127.0.0.1 localhost | 127.0.0.1 localhost | ||
Versione delle 19:34, 8 mar 2018
Premessa
Questo articolo potrebbe contenere inesattezze e/o dimenticanze, oltretutto e` la prima volta che uso e configuro 'hostapd' e 'dnsmasq'.
Si declina ogni responsabilita`.
Nell'esempio ho utilizzato la rete "192.168.3.0/24", cambiatela secondo le vostre neccessita`.
- Note
- Tutti i comandi ed i file sono da eseguire e/o modificare come utente "root".
- In alcuni ho aggiunto "sudo" davanti, ovviamente non e` necessario se gia` siete "root".
Installazione
Terminata l'installazione base Raspbian (fate eventuale aggiornamento), installiamo alcuni pacchetti necessari:
apt-get install hostapd hostap-utils dnsmasq
- iw
- nell'ultima release di Raspbian e` gia` installato, l'ho usato per controllare che la chiave usb wifi fosse AP compatibile (comando: "iw list", poi andate a leggere il report se compare la scritta AP)
Configurazione
Network
Per prima cosa ho modificato il file "/etc/network/interfaces" aggiungendo la configurazione per la periferica 'wlan0' (normalmente e` cosi` che viene vista la chiave usb wifi):
# interfaces(5) file used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8)
# Please note that this file is written to be used with dhcpcd
# For static IP, consult /etc/dhcpcd.conf and 'man dhcpcd.conf'
# Include files from /etc/network/interfaces.d:
source-directory /etc/network/interfaces.d
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
allow-hotplug eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
allow-hotplug wlan0
iface wlan0 inet static
address 192.168.3.1
netmask 255.255.255.0
hostapd /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf
hostapd
Letto "/usr/share/doc/hostapd/README.Debian", procediamo come indicato, generandoci dall'esempio il file "/etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf", per ragioni di permessi ho trovato qualche difficolta` ad eseguire il comando cosi` come scritto, questi dovrebbero funzionare:
sudo su zcat /usr/share/doc/hostapd/examples/hostapd.conf.gz > /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf
Per 'sicurezza' ho anche messo il file leggibile/scrivibile solo da 'root'
sudo chmod 600 /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf sudo chown root:root /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf
Ora correggiamo la configurazione secondo le nostre esigenze, modifichiamo "/etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf" (indichero` solo le righe che ho modificato, le altre sono state lasciate inalterate):
ssid=<MetteteUnNomePerLaReteWifi> wpa=2 wpa_passphrase=<MetteteLaVostra> wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK rsn_pairwise=CCMP
dnsmasq
Il procedimento e` lo stesso usato per la configurazione 'hostapd', utilizzo dell'esempio e modifiche del caso. Correggiamo la configurazione secondo le nostre esigenze, modifichiamo "/etc/dnsmasq.conf" (indichero` solo le righe che ho modificato, le altre sono state lasciate inalterate):
domain-needed bogus-priv interface=wlan0 dhcp-range=192.168.3.2,192.168.3.5,12h dhcp-option=option:router,192.168.3.1
Rimane solo un problema sulla risoluzione del nome macchina (hostname) di questo pc, al momento ho risolto sistemando il file "/etc/hosts" in questo modo, dove ho modificato la penultima ed aggiunto l'ultima riga (esempio reale preso da Centralina livello 1):
127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 127.0.1.1 level1error 192.168.3.1 level1
Firewall (iptables)
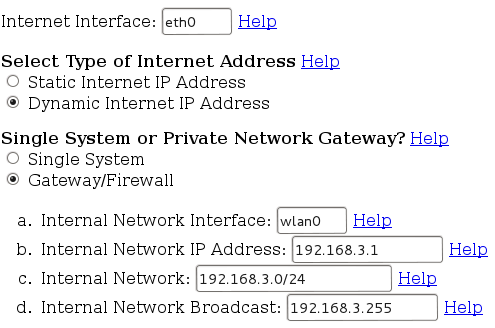
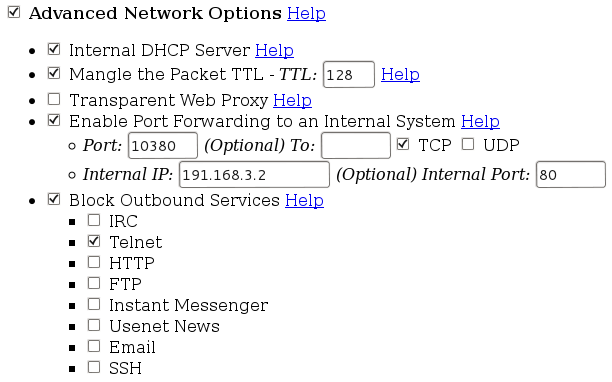
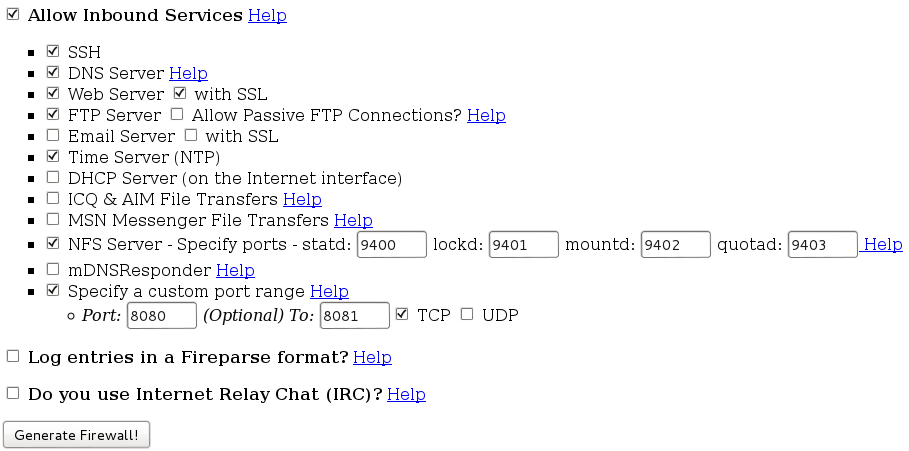
Normalmente uso un'utility online per generare la base e procedo poi al ritocco secondo le esigenze, l'indirizzo del 'generatore' e`: http://easyfwgen.morizot.net/
Questa e` la configurazione impostata, modificatela secondo le vostre esigenze, considerate sempre di NON usare e/o attivare opzioni che non conoscete e/o sapete a cosa servono. Da Notare che sono stati predisposti servizi che al momento non sono utilizzati, se pensate di non averne bisogno, disattivateli.
(Per migliorarne la lettura ho realizzato diverse schermate, che messe in ordine somigliano alla pagina web che vi troverete ad impostare).
Create la vostra configurazione e salvatela in un file chiamato "/etc/init.d/iptables", cambiate poi i permessi:
sudo chmod 755 /etc/init.d/iptables sudo chown root:root /etc/init.d/iptables
Questa e` quella che ho predisposto, attivando anche servizi come "http" ed "ftp":
#!/bin/sh
#
# Generated iptables firewall script for the Linux 2.4 kernel
# Script generated by Easy Firewall Generator for IPTables 1.15
# copyright 2002 Timothy Scott Morizot
#
# Redhat chkconfig comments - firewall applied early,
# removed late
# chkconfig: 2345 08 92
# description: This script applies or removes iptables firewall rules
#
# This generator is primarily designed for RedHat installations,
# although it should be adaptable for others.
#
# It can be executed with the typical start and stop arguments.
# If used with stop, it will stop after flushing the firewall.
# The save and restore arguments will save or restore the rules
# from the /etc/sysconfig/iptables file. The save and restore
# arguments are included to preserve compatibility with
# Redhat's or Fedora's init.d script if you prefer to use it.
# Redhat/Fedora installation instructions
#
# 1. Have the system link the iptables init.d startup script into run states
# 2, 3, and 5.
# chkconfig --level 235 iptables on
#
# 2. Save this script and execute it to load the ruleset from this file.
# You may need to run the dos2unix command on it to remove carraige returns.
#
# 3. To have it applied at startup, copy this script to
# /etc/init.d/iptables. It accepts stop, start, save, and restore
# arguments. (You may wish to save the existing one first.)
# Alternatively, if you issue the 'service iptables save' command
# the init.d script should save the rules and reload them at runtime.
#
# 4. For non-Redhat systems (or Redhat systems if you have a problem), you
# may want to append the command to execute this script to rc.local.
# rc.local is typically located in /etc and /etc/rc.d and is usually
# the last thing executed on startup. Simply add /path/to/script/script_name
# on its own line in the rc.local file.
###############################################################################
#
# Local Settings
#
# sysctl location. If set, it will use sysctl to adjust the kernel parameters.
# If this is set to the empty string (or is unset), the use of sysctl
# is disabled.
SYSCTL="/sbin/sysctl -w"
# To echo the value directly to the /proc file instead
# SYSCTL=""
# IPTables Location - adjust if needed
IPT="/sbin/iptables"
IPTS="/sbin/iptables-save"
IPTR="/sbin/iptables-restore"
# Internet Interface
INET_IFACE="eth0"
# Local Interface Information
LOCAL_IFACE="wlan0"
LOCAL_IP="192.168.3.1"
LOCAL_NET="192.168.3.0/24"
LOCAL_BCAST="192.168.3.255"
# Localhost Interface
LO_IFACE="lo"
LO_IP="127.0.0.1"
# Save and Restore arguments handled here
if [ "$1" = "save" ]
then
echo -n "Saving firewall to /etc/sysconfig/iptables ... "
$IPTS > /etc/sysconfig/iptables
echo "done"
exit 0
elif [ "$1" = "restore" ]
then
echo -n "Restoring firewall from /etc/sysconfig/iptables ... "
$IPTR < /etc/sysconfig/iptables
echo "done"
exit 0
fi
###############################################################################
#
# Load Modules
#
echo "Loading kernel modules ..."
# You should uncomment the line below and run it the first time just to
# ensure all kernel module dependencies are OK. There is no need to run
# every time, however.
# /sbin/depmod -a
# Unless you have kernel module auto-loading disabled, you should not
# need to manually load each of these modules. Other than ip_tables,
# ip_conntrack, and some of the optional modules, I've left these
# commented by default. Uncomment if you have any problems or if
# you have disabled module autoload. Note that some modules must
# be loaded by another kernel module.
# core netfilter module
/sbin/modprobe ip_tables
# the stateful connection tracking module
/sbin/modprobe ip_conntrack
# filter table module
# /sbin/modprobe iptable_filter
# mangle table module
# /sbin/modprobe iptable_mangle
# nat table module
# /sbin/modprobe iptable_nat
# LOG target module
# /sbin/modprobe ipt_LOG
# This is used to limit the number of packets per sec/min/hr
# /sbin/modprobe ipt_limit
# masquerade target module
# /sbin/modprobe ipt_MASQUERADE
# filter using owner as part of the match
# /sbin/modprobe ipt_owner
# REJECT target drops the packet and returns an ICMP response.
# The response is configurable. By default, connection refused.
# /sbin/modprobe ipt_REJECT
# This target allows packets to be marked in the mangle table
# /sbin/modprobe ipt_mark
# This target affects the TCP MSS
# /sbin/modprobe ipt_tcpmss
# This match allows multiple ports instead of a single port or range
# /sbin/modprobe multiport
# This match checks against the TCP flags
# /sbin/modprobe ipt_state
# This match catches packets with invalid flags
# /sbin/modprobe ipt_unclean
# The ftp nat module is required for non-PASV ftp support
/sbin/modprobe ip_nat_ftp
# the module for full ftp connection tracking
/sbin/modprobe ip_conntrack_ftp
# the module for full irc connection tracking
/sbin/modprobe ip_conntrack_irc
###############################################################################
#
# Kernel Parameter Configuration
#
# See http://ipsysctl-tutorial.frozentux.net/chunkyhtml/index.html
# for a detailed tutorial on sysctl and the various settings
# available.
# Required to enable IPv4 forwarding.
# Redhat users can try setting FORWARD_IPV4 in /etc/sysconfig/network to true
# Alternatively, it can be set in /etc/sysctl.conf
if [ "$SYSCTL" = "" ]
then
echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
else
$SYSCTL net.ipv4.ip_forward="1"
fi
# This enables dynamic address hacking.
# This may help if you have a dynamic IP address \(e.g. slip, ppp, dhcp\).
#if [ "$SYSCTL" = "" ]
#then
# echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_dynaddr
#else
# $SYSCTL net.ipv4.ip_dynaddr="1"
#fi
# This enables SYN flood protection.
# The SYN cookies activation allows your system to accept an unlimited
# number of TCP connections while still trying to give reasonable
# service during a denial of service attack.
if [ "$SYSCTL" = "" ]
then
echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_syncookies
else
$SYSCTL net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies="1"
fi
# This enables source validation by reversed path according to RFC1812.
# In other words, did the response packet originate from the same interface
# through which the source packet was sent? It's recommended for single-homed
# systems and routers on stub networks. Since those are the configurations
# this firewall is designed to support, I turn it on by default.
# Turn it off if you use multiple NICs connected to the same network.
if [ "$SYSCTL" = "" ]
then
echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/rp_filter
else
$SYSCTL net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter="1"
fi
# This option allows a subnet to be firewalled with a single IP address.
# It's used to build a DMZ. Since that's not a focus of this firewall
# script, it's not enabled by default, but is included for reference.
# See: http://www.sjdjweis.com/linux/proxyarp/
#if [ "$SYSCTL" = "" ]
#then
# echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/proxy_arp
#else
# $SYSCTL net.ipv4.conf.all.proxy_arp="1"
#fi
# The following kernel settings were suggested by Alex Weeks. Thanks!
# This kernel parameter instructs the kernel to ignore all ICMP
# echo requests sent to the broadcast address. This prevents
# a number of smurfs and similar DoS nasty attacks.
if [ "$SYSCTL" = "" ]
then
echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_broadcasts
else
$SYSCTL net.ipv4.icmp_echo_ignore_broadcasts="1"
fi
# This option can be used to accept or refuse source routed
# packets. It is usually on by default, but is generally
# considered a security risk. This option turns it off.
if [ "$SYSCTL" = "" ]
then
echo "0" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/accept_source_route
else
$SYSCTL net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_source_route="0"
fi
# This option can disable ICMP redirects. ICMP redirects
# are generally considered a security risk and shouldn't be
# needed by most systems using this generator.
#if [ "$SYSCTL" = "" ]
#then
# echo "0" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/accept_redirects
#else
# $SYSCTL net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects="0"
#fi
# However, we'll ensure the secure_redirects option is on instead.
# This option accepts only from gateways in the default gateways list.
if [ "$SYSCTL" = "" ]
then
echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/secure_redirects
else
$SYSCTL net.ipv4.conf.all.secure_redirects="1"
fi
# This option logs packets from impossible addresses.
if [ "$SYSCTL" = "" ]
then
echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/log_martians
else
$SYSCTL net.ipv4.conf.all.log_martians="1"
fi
###############################################################################
#
# Flush Any Existing Rules or Chains
#
echo "Flushing Tables ..."
# Reset Default Policies
$IPT -P INPUT ACCEPT
$IPT -P FORWARD ACCEPT
$IPT -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
$IPT -t nat -P PREROUTING ACCEPT
$IPT -t nat -P POSTROUTING ACCEPT
$IPT -t nat -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
$IPT -t mangle -P PREROUTING ACCEPT
$IPT -t mangle -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
# Flush all rules
$IPT -F
$IPT -t nat -F
$IPT -t mangle -F
# Erase all non-default chains
$IPT -X
$IPT -t nat -X
$IPT -t mangle -X
if [ "$1" = "stop" ]
then
echo "Firewall completely flushed! Now running with no firewall."
exit 0
fi
###############################################################################
#
# Rules Configuration
#
###############################################################################
#
# Filter Table
#
###############################################################################
# Set Policies
$IPT -P INPUT DROP
$IPT -P OUTPUT DROP
$IPT -P FORWARD DROP
###############################################################################
#
# User-Specified Chains
#
# Create user chains to reduce the number of rules each packet
# must traverse.
echo "Create and populate custom rule chains ..."
# Create a chain to filter INVALID packets
$IPT -N bad_packets
# Create another chain to filter bad tcp packets
$IPT -N bad_tcp_packets
# Create separate chains for icmp, tcp (incoming and outgoing),
# and incoming udp packets.
$IPT -N icmp_packets
# Used for UDP packets inbound from the Internet
$IPT -N udp_inbound
# Used to block outbound UDP services from internal network
# Default to allow all
$IPT -N udp_outbound
# Used to allow inbound services if desired
# Default fail except for established sessions
$IPT -N tcp_inbound
# Used to block outbound services from internal network
# Default to allow all
$IPT -N tcp_outbound
###############################################################################
#
# Populate User Chains
#
# bad_packets chain
#
# Drop packets received on the external interface
# claiming a source of the local network
$IPT -A bad_packets -p ALL -i $INET_IFACE -s $LOCAL_NET -j LOG \
--log-prefix "Illegal source: "
$IPT -A bad_packets -p ALL -i $INET_IFACE -s $LOCAL_NET -j DROP
# Drop INVALID packets immediately
$IPT -A bad_packets -p ALL -m state --state INVALID -j LOG \
--log-prefix "Invalid packet: "
$IPT -A bad_packets -p ALL -m state --state INVALID -j DROP
# Then check the tcp packets for additional problems
$IPT -A bad_packets -p tcp -j bad_tcp_packets
# All good, so return
$IPT -A bad_packets -p ALL -j RETURN
# bad_tcp_packets chain
#
# All tcp packets will traverse this chain.
# Every new connection attempt should begin with
# a syn packet. If it doesn't, it is likely a
# port scan. This drops packets in state
# NEW that are not flagged as syn packets.
# Return to the calling chain if the bad packets originate
# from the local interface. This maintains the approach
# throughout this firewall of a largely trusted internal
# network.
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp -i $LOCAL_IFACE -j RETURN
# However, I originally did apply this filter to the forward chain
# for packets originating from the internal network. While I have
# not conclusively determined its effect, it appears to have the
# interesting side effect of blocking some of the ad systems.
# Apparently some ad systems have the browser initiate a NEW
# connection that is not flagged as a syn packet to retrieve
# the ad image. If you wish to experiment further comment the
# rule above. If you try it, you may also wish to uncomment the
# rule below. It will keep those packets from being logged.
# There are a lot of them.
# $IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp -i $LOCAL_IFACE ! --syn -m state \
# --state NEW -j DROP
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp ! --syn -m state --state NEW -j LOG \
--log-prefix "New not syn: "
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp ! --syn -m state --state NEW -j DROP
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -j LOG \
--log-prefix "Stealth scan: "
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -j DROP
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL ALL -j LOG \
--log-prefix "Stealth scan: "
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL ALL -j DROP
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL FIN,URG,PSH -j LOG \
--log-prefix "Stealth scan: "
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL FIN,URG,PSH -j DROP
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL SYN,RST,ACK,FIN,URG -j LOG \
--log-prefix "Stealth scan: "
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL SYN,RST,ACK,FIN,URG -j DROP
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN,RST -j LOG \
--log-prefix "Stealth scan: "
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN,RST -j DROP
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,FIN SYN,FIN -j LOG \
--log-prefix "Stealth scan: "
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp --tcp-flags SYN,FIN SYN,FIN -j DROP
# All good, so return
$IPT -A bad_tcp_packets -p tcp -j RETURN
# icmp_packets chain
#
# This chain is for inbound (from the Internet) icmp packets only.
# Type 8 (Echo Request) is not accepted by default
# Enable it if you want remote hosts to be able to reach you.
# 11 (Time Exceeded) is the only one accepted
# that would not already be covered by the established
# connection rule. Applied to INPUT on the external interface.
#
# See: http://www.ee.siue.edu/~rwalden/networking/icmp.html
# for more info on ICMP types.
#
# Note that the stateful settings allow replies to ICMP packets.
# These rules allow new packets of the specified types.
# ICMP packets should fit in a Layer 2 frame, thus they should
# never be fragmented. Fragmented ICMP packets are a typical sign
# of a denial of service attack.
$IPT -A icmp_packets --fragment -p ICMP -j LOG \
--log-prefix "ICMP Fragment: "
$IPT -A icmp_packets --fragment -p ICMP -j DROP
# Echo - uncomment to allow your system to be pinged.
# Uncomment the LOG command if you also want to log PING attempts
#
# $IPT -A icmp_packets -p ICMP -s 0/0 --icmp-type 8 -j LOG \
# --log-prefix "Ping detected: "
# $IPT -A icmp_packets -p ICMP -s 0/0 --icmp-type 8 -j ACCEPT
# By default, however, drop pings without logging. Blaster
# and other worms have infected systems blasting pings.
# Comment the line below if you want pings logged, but it
# will likely fill your logs.
$IPT -A icmp_packets -p ICMP -s 0/0 --icmp-type 8 -j DROP
# Time Exceeded
$IPT -A icmp_packets -p ICMP -s 0/0 --icmp-type 11 -j ACCEPT
# Not matched, so return so it will be logged
$IPT -A icmp_packets -p ICMP -j RETURN
# TCP & UDP
# Identify ports at:
# http://www.chebucto.ns.ca/~rakerman/port-table.html
# http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers
# udp_inbound chain
#
# This chain describes the inbound UDP packets it will accept.
# It's applied to INPUT on the external or Internet interface.
# Note that the stateful settings allow replies.
# These rules are for new requests.
# It drops netbios packets (windows) immediately without logging.
# Drop netbios calls
# Please note that these rules do not really change the way the firewall
# treats netbios connections. Connections from the localhost and
# internal interface (if one exists) are accepted by default.
# Responses from the Internet to requests initiated by or through
# the firewall are also accepted by default. To get here, the
# packets would have to be part of a new request received by the
# Internet interface. You would have to manually add rules to
# accept these. I added these rules because some network connections,
# such as those via cable modems, tend to be filled with noise from
# unprotected Windows machines. These rules drop those packets
# quickly and without logging them. This prevents them from traversing
# the whole chain and keeps the log from getting cluttered with
# chatter from Windows systems.
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --destination-port 137 -j DROP
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --destination-port 138 -j DROP
# Network Time Protocol (NTP) Server
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --destination-port 123 -j ACCEPT
# DNS Server
# Configure the server to use port 53 as the source port for requests
# Note, if you run a caching-only name server that only accepts queries
# from the private network or localhost, you can comment out this line.
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --destination-port 53 -j ACCEPT
# If you don't query-source the server to port 53 and you have problems,
# uncomment this rule. It specifically allows responses to queries
# initiated to another server from a high UDP port. The stateful
# connection rules should handle this situation, though.
# $IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --source-port 53 -j ACCEPT
# Dynamic Address
# If DHCP, the initial request is a broadcast. The response
# doesn't exactly match the outbound packet. This explicitly
# allow the DHCP ports to alleviate this problem.
# If you receive your dynamic address by a different means, you
# can probably comment this line.
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --source-port 67 --destination-port 68 \
-j ACCEPT
# Network File System (NFS) Server
# Please note that additional services must
# be configured in order to support an NFS Server through
# the firewall. Read the help in the generator or this site:
# http://www.lowth.com/LinWiz/nfs_help.html
# NFS Server - portmapper
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --destination-port 111 -j ACCEPT
# NFS Server - statd
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --destination-port 9400 -j ACCEPT
# NFS Server - NFS daemon
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --destination-port 2049 -j ACCEPT
# NFS Server - lockd
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --destination-port 9401 -j ACCEPT
# NFS Server - mountd
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --destination-port 9402 -j ACCEPT
# NFS Server - quotad
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -s 0/0 --destination-port 9403 -j ACCEPT
# Not matched, so return for logging
$IPT -A udp_inbound -p UDP -j RETURN
# udp_outbound chain
#
# This chain is used with a private network to prevent forwarding for
# UDP requests on specific protocols. Applied to the FORWARD rule from
# the internal network. Ends with an ACCEPT
# No match, so ACCEPT
$IPT -A udp_outbound -p UDP -s 0/0 -j ACCEPT
# tcp_inbound chain
#
# This chain is used to allow inbound connections to the
# system/gateway. Use with care. It defaults to none.
# It's applied on INPUT from the external or Internet interface.
# DNS Server - Allow TCP connections (zone transfers and large requests)
# This is disabled by default. DNS Zone transfers occur via TCP.
# If you need to allow transfers over the net you need to uncomment this line.
# If you allow queries from the 'net, you also need to be aware that although
# DNS queries use UDP by default, a truncated UDP query can legally be
# submitted via TCP instead. You probably will never need it, but should
# be aware of the fact.
# $IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 53 -j ACCEPT
# Web Server
# HTTP
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 80 -j ACCEPT
# HTTPS (Secure Web Server)
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 443 -j ACCEPT
# FTP Server (Control)
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 21 -j ACCEPT
# FTP Client (Data Port for non-PASV transfers)
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --source-port 20 -j ACCEPT
# Passive FTP
#
# With passive FTP, the server provides a port to the client
# and allows the client to initiate the connection rather
# than initiating the connection with the client from the data port.
# Web browsers and clients operating behind a firewall generally
# use passive ftp transfers. A general purpose FTP server
# will need to support them.
#
# However, by default an FTP server will select a port from the entire
# range of high ports. It is not particularly safe to open all
# high ports. Fortunately, that range can be restricted. This
# firewall presumes that the range has been restricted to a specific
# selected range. That range must also be configured in the ftp server.
#
# Instructions for specifying the port range for the wu-ftpd server
# can be found here:
# http://www.wu-ftpd.org/man/ftpaccess.html
# (See the passive ports option.)
#
# Instructions for the ProFTPD server can be found here:
# http://proftpd.linux.co.uk/localsite/Userguide/linked/x861.html
# Sample Rule
# $IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 62000:64000 -j ACCEPT
# sshd
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 22 -j ACCEPT
# Network File System (NFS) Server
# Please note that additional services must
# be configured in order to support an NFS Server through
# the firewall. Read the help in the generator or this site:
# http://www.lowth.com/LinWiz/nfs_help.html
# NFS Server - portmapper
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 111 -j ACCEPT
# NFS Server - statd
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 9400 -j ACCEPT
# NFS Server - NFS daemon
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 2049 -j ACCEPT
# NFS Server - lockd
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 9401 -j ACCEPT
# NFS Server - mountd
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 9402 -j ACCEPT
# NFS Server - quotad
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 9403 -j ACCEPT
# User specified allowed TCP protocol
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 8080:8081 -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 10301:10302 -j ACCEPT
# Not matched, so return so it will be logged
$IPT -A tcp_inbound -p TCP -j RETURN
# tcp_outbound chain
#
# This chain is used with a private network to prevent forwarding for
# requests on specific protocols. Applied to the FORWARD rule from
# the internal network. Ends with an ACCEPT
# Block Outbound Telnet
$IPT -A tcp_outbound -p TCP -s 0/0 --destination-port 23 -j REJECT
# No match, so ACCEPT
$IPT -A tcp_outbound -p TCP -s 0/0 -j ACCEPT
###############################################################################
#
# INPUT Chain
#
echo "Process INPUT chain ..."
# Allow all on localhost interface
$IPT -A INPUT -p ALL -i $LO_IFACE -j ACCEPT
# Drop bad packets
$IPT -A INPUT -p ALL -j bad_packets
# DOCSIS compliant cable modems
# Some DOCSIS compliant cable modems send IGMP multicasts to find
# connected PCs. The multicast packets have the destination address
# 224.0.0.1. You can accept them. If you choose to do so,
# Uncomment the rule to ACCEPT them and comment the rule to DROP
# them The firewall will drop them here by default to avoid
# cluttering the log. The firewall will drop all multicasts
# to the entire subnet (224.0.0.1) by default. To only affect
# IGMP multicasts, change '-p ALL' to '-p 2'. Of course,
# if they aren't accepted elsewhere, it will only ensure that
# multicasts on other protocols are logged.
# Drop them without logging.
$IPT -A INPUT -p ALL -d 224.0.0.1 -j DROP
# The rule to accept the packets.
# $IPT -A INPUT -p ALL -d 224.0.0.1 -j ACCEPT
# Rules for the private network (accessing gateway system itself)
$IPT -A INPUT -p ALL -i $LOCAL_IFACE -s $LOCAL_NET -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A INPUT -p ALL -i $LOCAL_IFACE -d $LOCAL_BCAST -j ACCEPT
# Allow DHCP client request packets inbound from internal network
$IPT -A INPUT -p UDP -i $LOCAL_IFACE --source-port 68 --destination-port 67 \
-j ACCEPT
# Inbound Internet Packet Rules
# Accept Established Connections
$IPT -A INPUT -p ALL -i $INET_IFACE -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED \
-j ACCEPT
# Route the rest to the appropriate user chain
$IPT -A INPUT -p TCP -i $INET_IFACE -j tcp_inbound
$IPT -A INPUT -p UDP -i $INET_IFACE -j udp_inbound
$IPT -A INPUT -p ICMP -i $INET_IFACE -j icmp_packets
# Drop without logging broadcasts that get this far.
# Cuts down on log clutter.
# Comment this line if testing new rules that impact
# broadcast protocols.
$IPT -A INPUT -m pkttype --pkt-type broadcast -j DROP
# Log packets that still don't match
$IPT -A INPUT -m limit --limit 3/minute --limit-burst 3 -j LOG \
--log-prefix "INPUT packet died: "
###############################################################################
#
# FORWARD Chain
#
echo "Process FORWARD chain ..."
# Used if forwarding for a private network
# Drop bad packets
$IPT -A FORWARD -p ALL -j bad_packets
# Accept TCP packets we want to forward from internal sources
$IPT -A FORWARD -p tcp -i $LOCAL_IFACE -j tcp_outbound
# Accept UDP packets we want to forward from internal sources
$IPT -A FORWARD -p udp -i $LOCAL_IFACE -j udp_outbound
# If not blocked, accept any other packets from the internal interface
$IPT -A FORWARD -p ALL -i $LOCAL_IFACE -j ACCEPT
# Deal with responses from the internet
$IPT -A FORWARD -i $INET_IFACE -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED \
-j ACCEPT
# Port Forwarding is enabled, so accept forwarded traffic
$IPT -A FORWARD -p tcp -i $INET_IFACE --destination-port 80 \
--destination 191.168.3.2 -j ACCEPT
# Log packets that still don't match
$IPT -A FORWARD -m limit --limit 3/minute --limit-burst 3 -j LOG \
--log-prefix "FORWARD packet died: "
###############################################################################
#
# OUTPUT Chain
#
echo "Process OUTPUT chain ..."
# Generally trust the firewall on output
# However, invalid icmp packets need to be dropped
# to prevent a possible exploit.
$IPT -A OUTPUT -m state -p icmp --state INVALID -j DROP
# Localhost
$IPT -A OUTPUT -p ALL -s $LO_IP -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A OUTPUT -p ALL -o $LO_IFACE -j ACCEPT
# To internal network
$IPT -A OUTPUT -p ALL -s $LOCAL_IP -j ACCEPT
$IPT -A OUTPUT -p ALL -o $LOCAL_IFACE -j ACCEPT
# To internet
$IPT -A OUTPUT -p ALL -o $INET_IFACE -j ACCEPT
# Log packets that still don't match
$IPT -A OUTPUT -m limit --limit 3/minute --limit-burst 3 -j LOG \
--log-prefix "OUTPUT packet died: "
###############################################################################
#
# nat table
#
###############################################################################
# The nat table is where network address translation occurs if there
# is a private network. If the gateway is connected to the Internet
# with a static IP, snat is used. If the gateway has a dynamic address,
# masquerade must be used instead. There is more overhead associated
# with masquerade, so snat is better when it can be used.
# The nat table has a builtin chain, PREROUTING, for dnat and redirects.
# Another, POSTROUTING, handles snat and masquerade.
echo "Load rules for nat table ..."
###############################################################################
#
# PREROUTING chain
#
# Port Forwarding
#
# Port forwarding forwards all traffic on a port or ports from
# the firewall to a computer on the internal LAN. This can
# be required to support special situations. For instance,
# this is the only way to support file transfers with an ICQ
# client on an internal computer. It's also required if an internal
# system hosts a service such as a web server. However, it's also
# a dangerous option. It allows Internet computers access to
# your internal network. Use it carefully and only if you're
# certain you know what you're doing.
$IPT -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -i $INET_IFACE --destination-port 10380 \
-j DNAT --to-destination 191.168.3.2:80
###############################################################################
#
# POSTROUTING chain
#
$IPT -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o $INET_IFACE -j MASQUERADE
###############################################################################
#
# mangle table
#
###############################################################################
# The mangle table is used to alter packets. It can alter or mangle them in
# several ways. For the purposes of this generator, we only use its ability
# to alter the TTL in packets. However, it can be used to set netfilter
# mark values on specific packets. Those marks could then be used in another
# table like filter, to limit activities associated with a specific host, for
# instance. The TOS target can be used to set the Type of Service field in
# the IP header. Note that the TTL target might not be included in the
# distribution on your system. If it is not and you require it, you will
# have to add it. That may require that you build from source.
echo "Load rules for mangle table ..."
# Set the TTL in outbound packets to the same consistent value.
# A value around 128 is a good value. Do not set this too high as
# it will adversely affect your network. It is also considered bad
# form on the Internet.
$IPT -t mangle -A OUTPUT -o $INET_IFACE -j TTL --ttl-set 128
Faccio notare le due principali regole che abilitano "l'attraversamento" della rete (la navigazione, se possibile ovviamente, perche` il sistema a cui sto` lavorando non lo prevedera` visto che non intendo collegare la porta di rete 'eth0' da nessuna parte, anche se rimarra` disponibile e predisposta):
- echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
- Chiamato generalmente "forward", serve per ritrasmettere i pacchetti che devono attraversare/passare dalla rete locale ad un'altra
- $IPT -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o $INET_IFACE -j MASQUERADE
- Chiamato generalemnte "masquerade", funziona da mascheramento degli indirizzi della rete locale verso le altre.
Riavvio
- Importante
- Sconsiglio la modalita` di esecuzione dello script iptables come qua descritta, solo perche` non essendo in linea (o congruente, come dir si voglia) con gli altri script di avvio genera poi errori (solo a video) quando si installano e rimuovo altri pacchetti software.
- Suggerirei di posizionarlo in una directory differente, per esempio "/etc/myscripts/" ed avviarlo da "/etc/rc.local" (nda: Aggiungere link all'esempio che sara` in un nuovo 'progetto').
Be`, le modifiche sono state tante, avrei potuto riavviare tutti i servizi, ma ho optato per riavviare il Raspberry Pi.
Versione wheezy
Prima di riavviare ho installato il mio gestore di "init" preferito, per avviare "iptables" all'avvio del sistema:
sudo aptitude install sysv-rc-conf
Avete letto fra le descrizioni all'inizio del file che abbiamo generato vero ? Funziona con i comandi "start" e "stop", ma se provate ad utilizzare il comando ora "iptables" non comparira` fra i servizi, quindi riavviamo:
sudo reboot;exit
Autentichiamoci, eseguiamo:
sudo sysv-rc-conf
e attiviamo "iptables" al "runlevel 2", come da immagine (ci si sposta coi tasti freccia ed al punto desiderato si preme la barra spaziatrice, per uscire il tasto "q"):
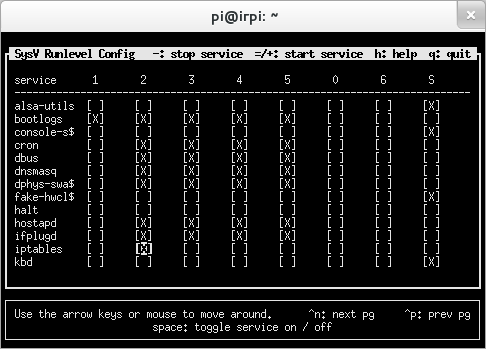
Ancora non era in avvio, dai prossimi riavii lo sara, ma ora dobbiamo avviarlo:
sudo service iptables start
Versione jessie
Ho modificato il firewall "/etc/init.d/iptables", aggiungendo all'inizio del file:
#!/bin/sh ### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: iptables # Required-Start: $hostapd # Required-Stop: # Default-Start: 2 3 4 5 # Default-Stop: # Short-Description: Run iptables firewall /etc/init.d/iptables if it exist ### END INIT INFO
- Ho scelto di avviarlo dopo "hostapd" perche` questo firewall l'ho usato per la "wlan", credo che funzioni ugualmente se specificato "network".
Poi ho dato i comandi:
sudo systemctl status iptables sudo systemctl enable iptables sudo update-rc.d iptables defaults
... e ho riavviato.
Per testare che sia in funzione, potete usare il comando:
sudo iptables --list
Test finale
Non resta che provare il collegamento da un client, mi raccomando di inserire il SSID e la Passphrase, quelle che avete utilizzato nella configurazione di "hostapd".
Problemi e FAQ
- Hostapd non si avvia
- Cercare il problema eseguendo il demone da linea di comando
sudo /usr/sbin/hostapd /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf
Riferimenti
- Articolo "Turn your Raspberry Pi into a Wireless Pi Point" su rivista The MagPi nr.11 (pagina 10)
- Raspberry PI come access point: l'esempio dell'AP usato al non-corso
- http://guide.debianizzati.org/index.php/Creare_un_Access_Point_con_Debian
- http://nims11.wordpress.com/2012/04/27/hostapd-the-linux-way-to-create-virtual-wifi-access-point/
- http://easyfwgen.morizot.net/